Submit Request ...
-
Forums
Understanding The Stages of Gum Disease
When you think of gum disease, you may picture a single condition with a specific set of symptoms. However, gum disease encompasses a range of different conditions that affect the tissue around your teeth. Both young and old people can be affected. If you suspect you have gum disease, it's important to understand its stages.
There are different stages of gum disease, with different treatment and management options. The prognosis for each stage depends largely on how advanced it is. Here, we look at the different stages of periodontal disease and the signs and symptoms associated with them.
What is gum disease?
Gum disease, often known as periodontal disease, is a dental condition that affects the gums around the teeth, leading to inflammation and infection. It is mainly caused by bacteria in the mouth. If not properly controlled, the growth of bacteria can turn into plaque and tartar. This hardened plaque can be acidic and cause the gradual destruction of the protective gum tissue and bone.
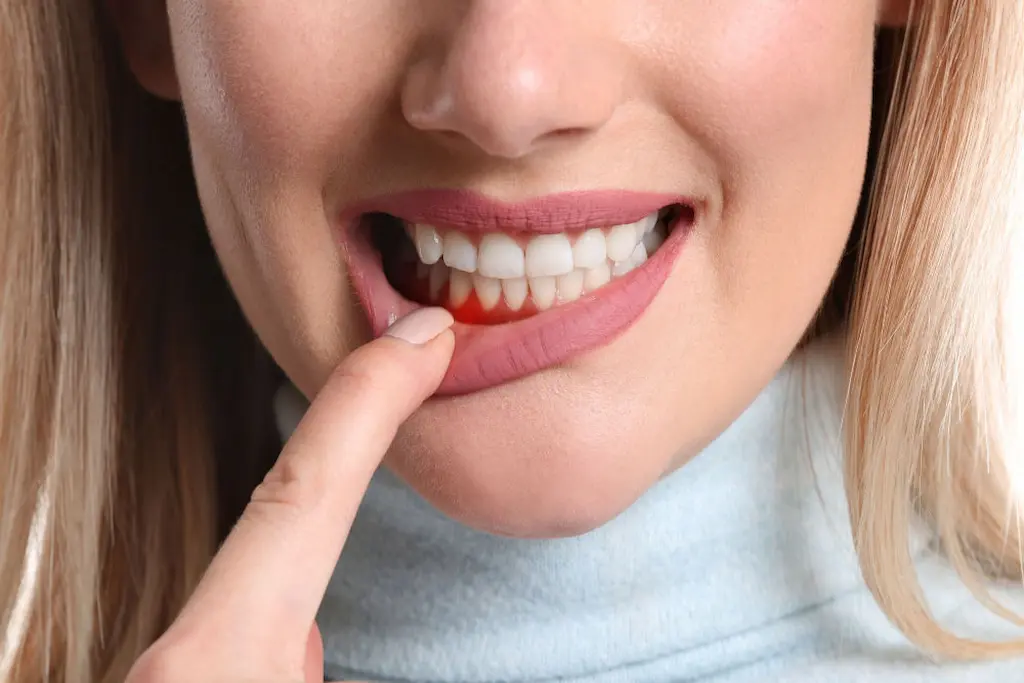
Bleeding
One of the first signs of gum disease is bleeding when you brush or floss. This may appear as pink spots on your toothbrush or bleeding after flossing. If you notice this, consult your dentist, as it may be an early sign of gum disease.
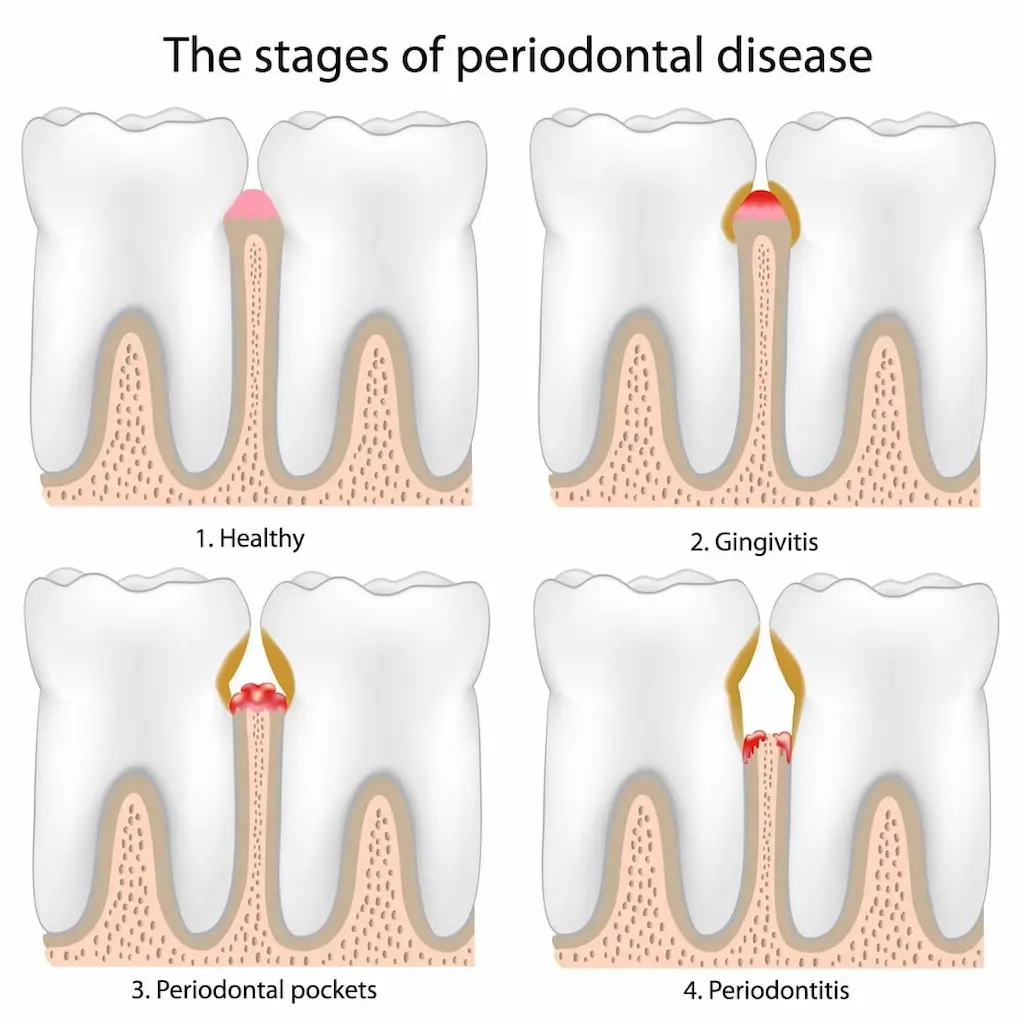
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the first stage of gum disease, which can cause swollen and painful gums. The gums may bleed or ooze pus due to plaque buildup along the gum line. With careful dental care, your dentist can remove plaque and possibly stop or even reverse the progression of gum disease.
Primary periodontitis
The third stage of gum disease is known as primary periodontitis. At this stage, people may experience painful and swollen gums. Plaque turns into tartar, which indicates decay. If left untreated, gum disease can damage the jawbone.

Moderate periodontitis
Moderate periodontitis, the fourth stage of gum disease, is characterized by receding, painful gums. Teeth are more susceptible to injury and decay more quickly. Teeth may become loose and the jawbone may become significantly infected. If you are at this stage, you may notice a foul-tasting discharge from inflamed gums. This is a serious condition and requires immediate dental advice.
Advanced periodontitis
The final stage, advanced periodontitis, can lead to tooth loss without prompt dental intervention. The infection can affect the jawbone and may lead to tooth loss. Chronic pain is a common symptom in advanced periodontitis.
Treatment
Early detection and treatment with antibiotics and thorough cleanings can effectively combat gum disease. However, long-term neglect makes gum disease harder to treat and reverse. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the infection.

Prevention
Regular dental checkups are crucial for early detection of gum disease and effective treatment to reverse any damage that may have occurred. Early stages, such as gingivitis, are common in adults over the age of 30 and can be managed with good oral care, including regular brushing, flossing, and using fluoride mouthwash. Regular dental visits are vital for detecting periodontal disease in its early stages and receiving appropriate treatment to prevent its progression.
Articles are reviewed by Dr. Moein Taghavi, a periodontal surgeon and periodontist. This information is for educational purposes only. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of a dentist, physician, or other qualified healthcare provider.
Please let us know what you think!